A commonly used and very important device that connects Multiple networks and forwards data packets between networks is a Network Router. Routers are responsible for directing data packets to their appropriate destinations, figuring out the safest and quickest route across the internet.
Routers facilitate internet connectivity, secure data transmission, and manage network traffic, whether in home networks, small businesses, or large enterprise infrastructures. Later in this guide, we’ll take a deeper look at the different types of routers, popular routing protocols, and what to look for when choosing the right router for your needs.

Network Routers: Your Most Pressing Questions
1. How Does a Router Work?

Routers work by examining the destination IP address of data packets and determining the most efficient route for the data to travel through multiple interconnected networks.
Routers contain a routing table used to help guide the forwarding of data across networks. They also perform functions like Network Address Translation (NAT) to facilitate one public IP address for many devices on a local network.
In enterprise branch network routers, the Router connects the local branch office network to the Main domain network, manages traffic and improves security.
Service provider routers serve an entirely different role, forwarding routers in multiple directions to and from the internet and ensuring that traffic can be delivered with high availability and speed to provide Internet service.
2. Routers, Modems, and Switches: What’s the Difference?

Router: Is used to route traffic between different networks, connecting local network to the internet, directing data to correct destination, and adding features like NAT and security.
Modem: Acts as a translator between the ISP’s network and your router so you can access the internet.
Switch: Transfers data between devices in the same local network, working on MAC addresses.
More details between router and switch, please check the previous articles: Router vs. Switch: What’s the Difference and Which One Do You Need?
3. Router and Wi-Fi: What’s the Difference?
A router is not the same as Wi-Fi. A router is a physical device that routes data between networks; Wi-Fi is a wireless technology that allows devices to connect to a network without cables.
A router typically includes Wi-Fi capabilities, but serves a unique functionality within a network.
Types of Routers
Core Router
Core routers are built for large-scale traffic routers, serving within the backbone of an enterprise network. These routers are fast and transfer packets quickly across service provider routers as well as between branch offices of a corporation.
You can take Cisco ASR 9000 Series for example, this router is used mainly as high-performance core router for large enterprises or service providers.
Edge Router
Edge Routers: Edge routers are located at the edge of an organization’s network, allowing it to connect to other networks (e.g., the internet or other networks). These routers play an essential role in branch networks, especially those in small offices.
Huawei AR Series routers are ideal for building edge routing solutions, allowing a branch office network to connect to the core network while ensuring secure traffic management.

Distribution Router
These routers combine traffic from several access routers, c and network routers.
The Juniper MX Series is another common type of router used for distribution routing in enterprise networks, in between client and data center areas in the overall network.
Wireless Router
A wireless router is just a router that also includes a wireless access point aka Wi-Fi.
A popular option, the HPE Aruba 5000 Series, offers high-speed routing with strong wireless support for wired and wireless connected devices.
Virtual Router

Virtual (software) routers based routers are software-based, and are designed to offer more flexibility in cloud environments and virtualized networks.
Things to Consider When Choosing the Right Network Router Industrial routers in all RG-S5750G Series achieve exceptional price-performance ratios and scalable virtual router capabilities, making them a cornerstone of future virtualized data center networks.
Main Types of Routing Protocols and Examples
Routing protocols define how routers exchange routing information among themselves. Here are the most popular routing protocols used in enterprise branch networks and service provider routers:

Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Routing Information Protocol (RIP): An old distance-vector routing protocol that is easy to configure and has some limitations on scalability It is usually found in smaller networks or home routers for basic operations.
Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP)
IGRP, designed by Cisco, is a distance-vector protocol responsible for routing within an autonomous system and works well for enterprise branch routers. Uses several metrics, such as bandwidth and delay, to compute the best route.
EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol) is a more advanced interior gateway routing protocol than IGRP and the Cisco proprietary protocol. RIPng combines aspects of distance-vector and link-state routing, and is popular among service provider routers for its high scalability and fast convergence.
OSPF – Open Shortest Path First
Link-state routing protocol; OSPF is widely adopted in large enterprise networks as it is highly scalable. This is used to make guarantee that informs are taken the briefest conceivable way over the system.
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
For service provider routers BGP is a core internet routing protocol. It is essential to Internet backbone routers, helping direct traffic between autonomous systems.
Data link layer Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP)
EGP is mainly used when we need to route between different networks, especially in large service provider routers where external connectivity is needed.
IS-IS (Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System)
It is a link-state routing protocol hated by many in large-scale service provider networks as it is similar to OSPF and has high scalability and stability.
Why Do We Need a Router?
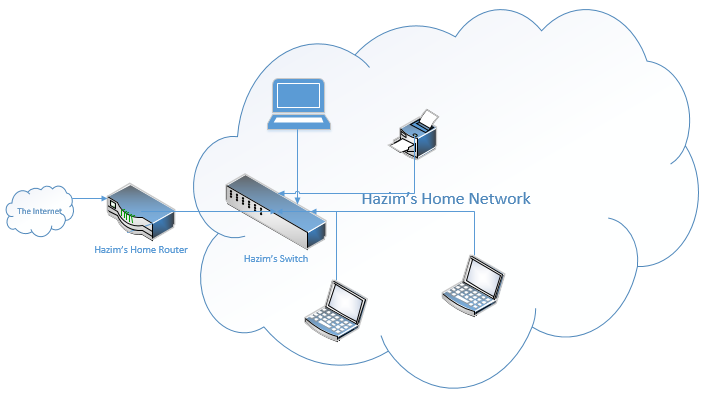
Here are a few reasons why routers are important to enterprise networks, branch offices, and small businesses:
Inter-Networking
Routers also play an essential role in connecting multiple individual networks together to form an internetwork, allowing for communication between networks.
Traffic Control
Routers help organize traffic, making decisions about how data should travel between networks, and sending it on the fastest path.
Security
Most routers have built-in features like firewalls, automatically detecting and neutralizing security threats.
How to Choose the Best Router for Your Home or Business?
The most suitable router for you can depend on how many devices you have, how your home network is set up and what security features you need. Here are some key factors to help you making decision:
Connectivity
Wifi: Check how many of the aforementioned Ethernet or Wi-Fi standards the router supports. The Cisco ISR 4000 Series routers, for example, deliver enterprise-level connectivity with multiple WAN options.
Bandwidth
Choose a router that’s capable of keeping up with your network bandwidth needs, whether you’re supporting video conferencing in a business network or running a gaming setup at home.
Wireless Capability
Identify high performance simple routers for home networks or small business routers, all in ones like Ruijie RG-S2924G allow better Wi-Fi performance just like Wi-Fi 6 provide added speed and coverage.
Easier to set up and manage
The convenience factor is particularly important, so generally pick routers that come with easy, user-friendly interfaces, great, easy-to-follow setups. Easy to manage, particularly for small businesses – HPE Aruba 2930F Series
Security
Consider a router that offers security features (VPN support, firewalls, encrypted connections, etc.) to safeguard sensitive data. To address some issues, let you train on your own data up to October 2023.
Flexibility
Think about future expansion potential of the router. Huawei AR Series routers offer soft and hard scalability options to meet the needs of growing businesses or enterprise networks.
Automatic Updates
Get routers with automatic firmware updates to make sure security patches are applied as quickly as possible.
Mesh Networks
If you have a big home or operate an office, look at routers that support mesh networking. TP-Link Deco M9 Plus mesh network setup.

Guest Networks
Guest networking functionality is overnight for most businesses and also in home networks so that visitors can access the internet without compromising the security of your main network.
QoS (Quality of Service) Controls
Check that your router supports QoS config, to enable you to prioritize bandwidth use for vital applications, like video calls or VoIP services.
Conclusion
Choosing the right router for you is crucial for network performance, security and scalability. Whether you need to set up home network, a small office or a larger enterprise system, having the right router in place means you have a secure, efficient, reliable network infrastructure. Companies like Cisco, Juniper, Ruijie, Huawei and HPE provide specialized routers with different purposes as well as performance/ security/ scalability in mind.
Did this article help you understand network switches and how they work? Tell us on Facebook and LinkedIn . We’d love to hear from you!


 https://network-switch.com/pages/about-us
https://network-switch.com/pages/about-us
