Today, Ethernet switches play a very important role in networking as the backbone that links all devices in a network. The ports of these switches are capable of supporting different data rates, network types and network functions. Subcategory The different types of Ethernet switch ports are very important to know if you're planning to optimize network performance and ensure that your devices will be compatible.

What is an Ethernet Switch Port?
An Ethernet switch port is a physical connection on a network switch used to transmit data between devices. These ports may be different in speed, features and the connector they are compatible with. Port type selection is critical in achieving both network performance as well as scalability you desire.
Data Speed vs. Various Types of Ethernet Switch Ports
The Ethernet switch port were divided into groups depending on what they were rated. The below types of ports are classified based on their data rates:
RJ45 Port
- Data Rate: Up to 1 Gbps
- Media Type: Copper (Cat5e, Cat6 cable)
- Application: Perfect for short range networking in small to medium sized networks.
SFP Port
- Rate: Up to 1 Gbps commonly
- Media Type: Fiber or copper (using SFP transceivers)
- Applicable to: Connect the fiber network, and have the long distance copper transmitting function.

SFP+ Port
- Data Rate: Up to 10 Gbps
- Media Type: Fiber or copper. High-performance, fiber optic components for existing and next generation, 2.5 and 10 Gbps datacom and telecom systems.
- Use Case: Found in datacenters and in the core of enterprise networks needing more bandwidth.
SFP28 Port
- Data Rate: Up to 25 Gbps
- Media Type: Fiber or copper (with SFP28 transceivers)
- Use case: Promising new standard for Hi-speed applications.
QSFP+ Port
- Data Rate: Up to 40 Gbps
- Media Type: Fiber (using QSFP+ transceivers)
- Use Case: Ideal for HPC and data center interconnects.
QSFP28 Port
- Data Rate: Up to 100 Gbps
- Media: Fiber (using QSFP28 transceivers)
- Use Case: Supports 100G Ethernet, suitable for large-scale data centers.
CFP Port
- Data Rate: Up to 100 Gbps
- Media Type: Fiber (with CFP transceivers)
- Use Case: Used mostly in highcapacity and telecom networks.
QSFP-DD Port
- Data Rate: Up to 400 Gbps
- Media Type: Fiber(with QSFP-DD transceivers)
- Use Case: 400G Ethernet compatible, intended for future data centers.
SFP-DD Port
- Data Rate: Up to 400 Gbps
- Both port rows are populated with Fiber (via SFP-DD transceivers)
- Use Case: Yielding higher total capacity when compared to QSFP-DD, ideal for high-capacity solutions.
OSFP Port
- Data Rate: Up to 400 Gbps
- Type: Fiber (with OSFP transceivers)
- Use Case: Dense, high-performance data center.
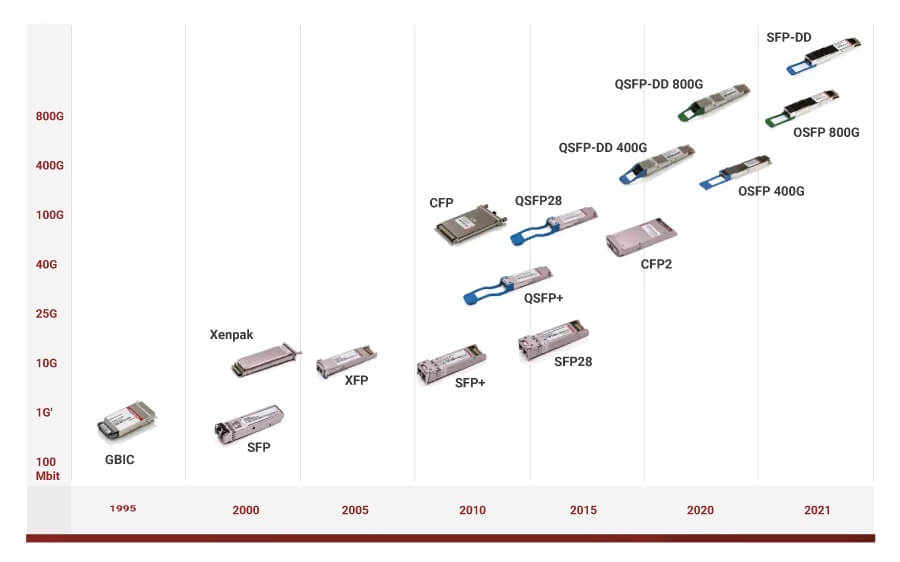
Different Ethernet Switch Port Types by Network Architecture
Switch ports can also be categorized according to their usage in network topology:

Access Port
- Function: This port connects host devices (i.e. computers or printers) to one VLAN.
- Properties: Sends untagged frames, usually the unicast Destination MAC addresses of endpoints.
- Practical Application: Perfect for connecting devices to power source the network separately.
Trunk Port
- Function: Carries traffic for multiple VLANs between switches.
- Features: Sends tagged packets; Allows tagged information through.
- Use Case: When used between switches to prevent VLAN bleeding.
Hybrid Port
- Function: Hybrid of access and trunk features.
- Features: Can support tagged and untagged frames.
- Use Case: Can be handy when port using for end user and inter-switch is the requirement.
Function Based Types of Ethernet Switch Port Types
Ports of Ethernet Switches may also be classified according to function:
PoE Port ( Power over Ethernet)
- Function: Supply power AND data transfer between your Power over Ethernet (PoE) devices using this cable.
- Standards: IEEE 802.3af, /g/ /u at /PoE /PoE+ /PoE++.
- Use Case: Ideal for powering devices like IP cameras, VoIP phones, and wireless access points.
Combo Port
- Function: On of ports (e.g., RJ45 port and SFP port) save the others internal resources.
- Features: only support one port; Provide for connecting options.
- Use Case: It is applicable when you want pins for different media types and the number of ports is constrained.
Stack Port
- Function: Can connect multiple switches to operate together.
- Features: Allow for central management and increase the number of ports.
- Use Case: Perfect for growing your network with a solution that demands optimal performance for greater complexity.
Final Thoughts
Knowing the different Ethernet switch port types is important for an optimal network design and utilization. Depending on data speed, network architecture and use case, you can optimize performance, scalability and manageability using the right port types. Whether you are building a small office network or a large datacenter, you need to select the best switch to meet your needs as well as budget.
Did this article help you understand network switches and how they work? Tell us on Facebook and LinkedIn . We’d love to hear from you!


 https://network-switch.com/pages/about-us
https://network-switch.com/pages/about-us


