Digital infrastructure Data centers are the heart of the modern IT world – driving the apps and services on which we depend for our personal and professional lives. Description Knowledge of data center architecture is fundamental for companies trying to optimize performance, scalability, and uptime.
Key Data Center Architecture Building Blocks
The components of a data center architecture help facilitate the delivery of IT services including infrastructure applications and end-user applications. Key elements include:
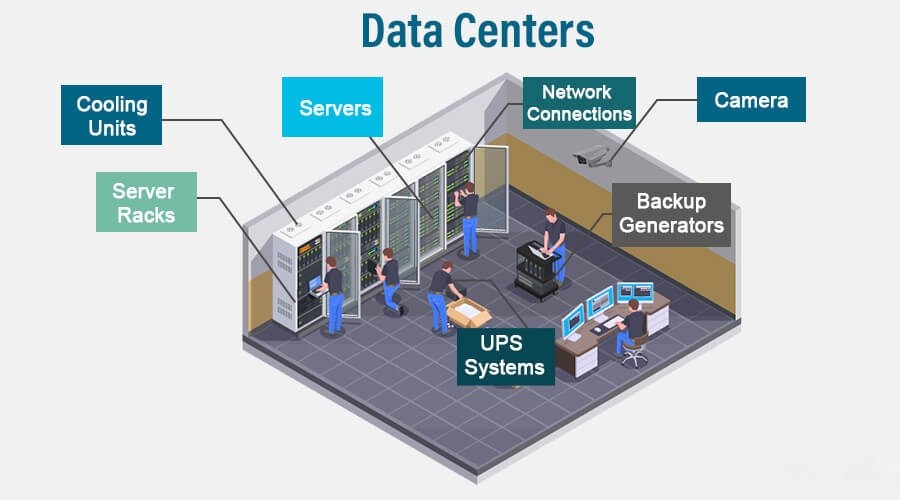
Compute - Servers: Processors of the application / service.
Storage: Methods and technologies for storing data, including SAN and NAS.
Network Infrastructure: Routers, switches and firewalls that assist in data movement and connectivity.
Electricity: UPS and generator, to guarantee full time operation.
Cooling: Systems like heating, ventilation and air conditioning, which regulates temperature and humidity.
Security: Action that will be taken to protect data and investment in physical and cyber security of infrastructure.
The problem is that these pieces need to be designed to interoperate in order to provide high availability and high performance.
Data Center Architecture Types
Data center design Archetypal data center, Overhead view of an architect's rendering Archetypal data center, Depending on how it is classified, a data center can serve a certain type of a user (digital services, government, etc). Below are some common types:
Three-Tier Architecture

A classical modell of comprising:
Core Layer: Fast backbone that ties the segments of the network together.
Aggregation Layer: All switches that collect connections one closer to the access layer.
Access: Where end user devices connect to the network.
This type of architecture can be better under structure; however, some latency among multiple hops may be introduced.
Leaf-Spine Architecture
A modern approach featuring:

Leaf Switches: Connect to your servers and other devices.
Spine Switches: That connect leaf switches while facilitating data flow.
This type of architecture lowers latency and improves scalability by reducing the number of hops between endpoints.
ToR Architecture
AddTransient-oriented computing also need to be addressed in the singlecluster setting.

ToR Switches: Placed at the top of server racks, connecting all servers within the rack.
This design makes for easier cabling and is very affordable for small to medium data centers.
Hyper-Converged Infrastructure (HCI)

Hyper-Converged Infrastructure (HCI) itself refers to the aggregation of infrastructure resources (computing, storage, networks) and the computing and management functions that controllers bring.
Integrates compute, storage and networking in one system:
Software-Defined: Makes extensive use of software for resource control.
Scalable: It can grow by the addition of nodes.
Perfect for companies that need the freedom, and to easily and effectively manage their business.
Software-Defined Data Centre (SDDC)

A concept remains to be the driver of the physical cloud datacentre operational model – that of software-defined infrastructure (SDI).
An advanced model where:
Virtualization – everything is virtualized in the infrastructure.
Automation: It is software driven management.
Offers flexibility and speed, but demands advanced management tools.
Considerations on Data Center Network Design Choices
When architects a network these days there are a few things that needs to be taken into account:
It is also about scalability, being able to stash a certain amount of resources to serve the demand increase.
Redundancy: adding secondary systems for backup in order to continue running in case the primary system goes down.
Latency: Reducing processing time for data transfer.
Security: This is about securing data and infrastructure from threats.
Energy Saving: Lower the power consumption and less cooling cost.
No compliance: Not meeting industry standards or regulations.
Optimizing these trade-offs is essential for creating a strong and cost-effective data center.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Data Center Architecture
This vendor-agnostic guide will help you easily understand data center design and determine how to design your data center to optimize available resources.
Q1: What is the difference between a data center and a server farm?
Answer: A server farm is a collection of servers that sit in the same site; however, a data center is a larger site which houses not just servers but networking gear, storage, power, HVAC and cooling systems, and other equipment.
Q2: What enables the high availability of data centers?
Answer: Datacenters keep running despite failing components through redundancy by having multiple power supplies, backup generators and failovers.
Q3: How do you see virtualization impacting data center design?
Answer: Facilitates the efficient use of resources by running multiple virtual machines on a single physical host, and also simplifies the use of physical space and electrical power.
Q4: What about security in a data center?
Answer: Data center security includes security measures such as surveillance and access control to physical security facilities and cybersecurity defenses to defend against cyberattacks and data breaches.
Q5: Why is cooling important in data center infrastructure design?
Answer: Cooling Efficiency for preventing your computer 's components from Overheating and the cool air ensures long-term usable PC parts.
Did this article help you or not? Tell us on Facebook and LinkedIn . We’d love to hear from you!


 https://network-switch.com/pages/about-us
https://network-switch.com/pages/about-us


